The Hyrcanian mixed Forests are a green belt of predominantly temperate deciduous forests stretching over the northern slopes of the Alborz mountain range, along the southern borders of the Caspian Sea. They stretch across three provinces of Iran (Gilan, Mazandaran and Golestan) from Astara in the northwest to the vicinity of Gorgan (Golidaghi) in the northeast of Iran, and also include a small western portion in the country of Azerbaijan.
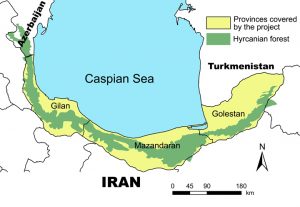
Based on the latest data from the Forests, Rangelands and Watershed Organization (FRWO) the Caspian Hyrcanian mixed Forests are approximately 800 km long and 110 km wide, with a total area of 1.85 million ha. They comprise 15% of the total Iranian forests and 1.1% of the country‟s area (Sagheb Talebi et al., 2014). The Hyrcanian forests rise from sea level up to an altitude of 2,800 m and encompass a variety of different forest types. The term “Hyrcanian” came from the word “Hyrcan”, which means wolf land.
The role of Caspian Sea
The remarkable Hyrcanian Forests only exist because of the mass of water vapors that evaporate from the Caspian Sea. When these confront the Alborz massif, it acts as a climatic wall, producing dense clouds and discharges of rain or snow; this, in turn, creates a very dense forest on the northern slope of the Alborz Mountains, while the southern slopes end in the Kavir desert, one of the driest deserts in the world (Knapp, 2000).
The Caspian region (forest and non-forest habitats) is known for the rich diversity and endemism of its flora, with 3234 species recorded to date, this being 44% of the entire floral species of Iran.
Fauna of Caspian Hyrcanian mixed Forest
The Caspian forests support an important assemblage of large mammals including the Endangered Persian leopard, brown bear, wolf, red deer, roe deer. The last Caspian tiger was killed in 1958.
The Hyrcanian mixed forests support a rich assemblage of bird species typical of broad-leaved temperate forests, including the near endemic Caspian tit Parus (Poecile) hyrcanus, and an important assemblage of forest specialist species. There are also 31 species of reptiles, nine species of amphibians and 53 species of fish. Invertebrate populations are poorly known.

Main treat to Hyrcanian Forests
The main threat to the biodiversity of the Hyrcanian Forests arises from habitat loss and fragmentation arising from conversion of forests to agricultural and urban land, private dwellings, dam construction etc.
Other threats include unsustainable timber harvest, firewood collection, climate change (pests and diseases, forest fires), and pollution / garbage dumping.
Reference: Biodiversity of the Hyrcanian Forests: A synthesis report

Gileboom homestay located in a village named Qasem-Abad with wide range of Flora and fauna of Caspian Hyrcanian mixed forest. The Sarve-Lat protected area and the diversity of trees and plants make the village an extraordinary place.
If you would like to have a hiking or trekking in the Hyrcanian mixed Forests: please check the links below and call us in Whatsapp or send us an email:






